Windows 95 / 98
The EMS driver is called by the MS-DOS command processor Command.com to provide 64kbyte pages of RAM from the Windows operating system memory pool (which may contain many megabytes of spare memory).
When an MS-DOS window is started, COMMAND.COM is executed. You can check whether EMS is installed by right clicking on the title bar of the window and selecting "properties"
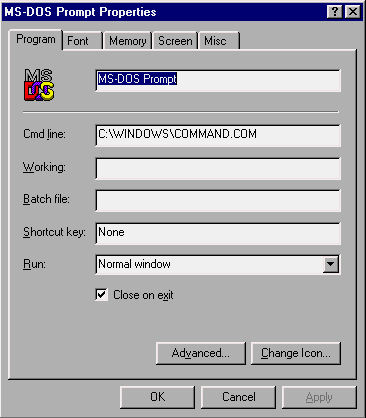
On most PCs running Windows 95 or 98, COMMAND.COM in will be in the C:\WINDOWS, but sometimes there will be an additional copy in the root directory C:\. Select the "memory" tab.
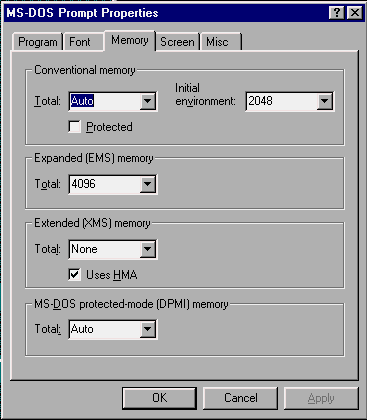
You should set the EMS memory to the minimum required by the MS-DOS programs that you are going to run. Remember that while the MS-DOS window is open, the EMS memory allocated will not be available to other windows. Note that the maximum for EMS memory is 16.384 Megabytes.
Before you can allocate EMS memory in this way, an EMS driver must be installed on the system. The default Windows 95/98 setup installs the driver, but some program installations (Novell Netware client for example) may make it necessary to provide an EMS driver at startup. To install the drivers, add the following to lines to the file CONFIG.SYS in the C:\ root directory :-
DEVICE=C:\WINDOWS\HIMEM.SYS DEVICE=C:\WINDOWS\EMM386.EXE
You will need to re-boot the computer before the changes can take effect.
