Back to:
LEA applications use tables in Oracle and dBASE format.
dBASE tables are stored as individual files, with associated memo and index files for each table stored as separate files with the same file prefix as the table file name. dBASE tables are a simple portable format widely recognised by many different software products, such as Microsoft Office and ESRI ArcView. There are a number of different versions of the dBASE format - LEA applications will read all versions, but by default will create dBASE IV files. Other software products may not recognise later dBASE format versions.
Oracle is the leading client/server database. Applications which
use data from Oracle databases have very little control over the internal data
storage, so application performance is very dependent on the configuration and
load of the database server. LEA applications support Oracle 8i and Oracle 9i.
For best performance, the Oracle client software (available from
www.oracle.com) should be installed on each
PC. However, LEA applications can access Oracle databases directly without the
need for the Oracle client software if necessary.
All proprietry database formats have slightly different restrictions on legal names for tables, fields and indexes. When creating or copying tables, LEA applications will check that names are valid for the current database type, but may not be able to translate names into a more restrictive database.
With all databases, each field name must be unique within the table, and although most formats differentiate between upper- and lower-case characters, it is usually best to assume that field names differing only in the case of the characters will not be considered unique.
Following is a table summarising the main field naming restrictions for supported LEA database formats, and other common formats.
Database Max field name length Legal characters Other restrictions dBASE 10 characters Upper-case letters A-Z, digits 0-9 and underscore ('_') Oracle 30 characters Lower-case and upper-case letters a-z and A-Z, digits 0-9
underscore ('_')
dollar symbol ('$')
hash symbol ('#')Field name must begin with a letter Access 64 characters All except period ('.'), exclamation mark ('!'),
back quote ('`') and square brackets ('[' and ']')Field name cannot start with a space Informix 18 characters Lower-case and upper-case letters a-z and A-Z, digits 0-9 and underscore ('_') Field name must begin with a letter InterBase & Firebird 31 characters Lower-case and upper-case letters a-z and A-Z, digits 0-9
underscore ('_')
dollar symbol ('$')Field name must begin with a letter Paradox 25 characters All except comma (','), pipe ('|') and exclamation mark ('!') Field name cannot begin with a space Sybase 30 characters Lower-case and upper-case letters a-z and A-Z, digits 0-9
underscore ('_')
dollar symbol ('$')
hash symbol ('#')Field name must begin with a letter
dBASE lacks the concept of a distinct primary key which provides a default sort order and unique records for a table.
All secondary indexes created on dBASE tables by LEA applications will be maintained indexes, stored in a file with extension .mdx. Non-maintained (.ndx) indexes will not be used.For Oracle databases each index name must be unique within the database. LEA applications create a unique primary key name where necessary by naming the primary key 'PK_' followed by the table name.
LEA applications provide a standard mechanism for opening and saving database tables using a customised file selection dialogue.
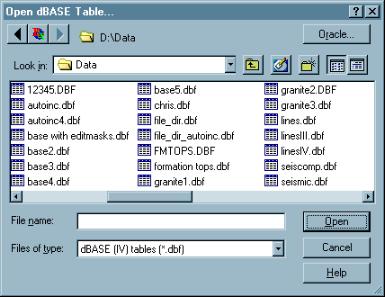
This dialogue allows selection of dBASE tables
All files of the selected type in the current folder are displayed. In the Open dialogue, you must select an existing file. In the Save dialogue, enter a new name in the edit box to create a new file, or select a file from the list to overwrite it.
The buttons in the top-left corner of the dialogue provide standard LEA directory navigation (as described in System Library - File Selection dialogues).
The Oracle... button opens the Oracle Table Selection dialogue (below).
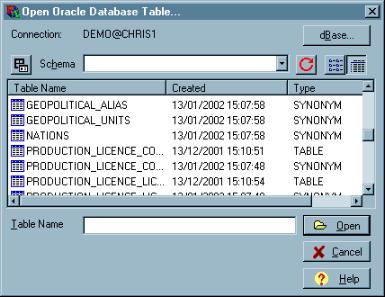
This dialogue allows browsing of all available Oracle databases. When this dialog first appears, it will attempt to connect to the default Oracle database (specified by the default oracle database key in the [startup] section of DBUTILS.INI) using the current Windows user name. If this fails, a connection dialog will be displayed. Enter a valid username, password and database to connect to the Oracle server.
The drop-down combo-box displays a list of the available schemas for the current Oracle database. The default schema is blank - this will show all tables (and views and synonyms) belonging to the current user, plus all public synonyms. To view tables belonging to another user, for which public synonyms do not exist, select that schema from the combo-box.
Not all public synonyms are displayed in the default schema. The dialogue attempts to cut down the number of objects displayed by excluding synonyms of objects belonging to a list of users specified in the DBUTILS.INI by the oracle exclude users key in the [startup] section.The dBase... button will return you to the dBASE table selection above.
The Connectbutton displays a drop-down menu to disconnect the current Oracle connection, or display a connection dialogue to enter a new user-name, password and database.
The Refreshbutton will re-fetch the list of tables from the database.
The Listbutton displays just the name of all available tables.
The Detailsbutton displays the name and creation date of all available tables, synonyms and views.
LEA applications usually require the Oracle client software (version 8
or 9) to be installed on the PC. The Oracle client must be configured correctly
on the PC - see your Oracle documentation for details of how to do this. The
Oracle client software contains a number of utilities which may be useful for
low-level database monitoring and maintenance. Client software for different
operating systems and hardware platforms can be downloaded from
www.oracle.com.
The name of the Oracle
database to connect to be default is specified by the default oracle
database key in the [startup] section of DBUTILS.INI. This
should usually be the TNS alias you use if connecting using Oracle SQL*Plus. By
default, LEA applications will attempt to connect to Oracle using the current
Windows user-name. If the database is not configured to use the current OS
user, or there is no matching Oracle , a login dialogue will be displayed when
you can enter a user name and password for authentication by the Oracle
database.
LEA applications can also access an Oracle database via TCP/IP without requiring the Oracle client software to be installed. To enable this, the allow oracle net key in the [startup] section of DBUTILS.INI must be set to a non-zero value (ie 'true') and the default oracle net key should specify the connection string to use for a direct TCP/IP connection. The connection string is a colon-delimited list of the address of the Oracle server (hostname or IP address), the port number on which the Oracle listens, and the SID of the database instance, eg SERVER_1:1521:ORACL.
LEA programs also allow the Oracle connection string to be specified on
the command-line.
The -u switch allows you to specify
USERNAME/PASSWORD@TNSALIAS, and the -remote switch allows you to specify
a TCP/IP connection without using the Oracle client:
TBLVIEW -u/@ORACL
or
TBLVIEW -remote -uSCOTT/tiger@SERVER_1:1521:ORACL
If you are having problems connecting to Oracle with LEA applications, check the following:
The following list of words are reserved for use in Oracle (Release 9) SQL commands and statements, and will cause errors if you attempt to name tables or fields with them.
| ACCESS ADD ALL ALTER AND ANY AS ASC AUDIT BETWEEN BY CHAR CHECK CLUSTER COLUMN COMMENT COMPRESS CONNECT CREATE CURRENT DATE DECIMAL DEFAULT DELETE DESC DISTINCT DROP ELSE |
EXCLUSIVE EXISTS FILE FLOAT FOR FROM GRANT GROUP HAVING IDENTIFIED IMMEDIATE IN INCREMENT INDEX INITIAL INSERT INTEGER INTERSECT INTO IS LEVEL LIKE LOCK LONG MAXEXTENTS MINUS MLSLABEL MODE |
MODIFY NOAUDIT NOCOMPRESS NOT NOWAIT NULL NUMBER OF OFFLINE ON ONLINE OPTION OR ORDER PCTFREE PRIOR PRIVILEGES PUBLIC RENAME RESOURCE REVOKE RAW ROW ROWID ROWNUM ROWS SELECT SESSION |
SET SHARE SIZE SMALLINT START SUCCESSFUL SYNONYM SYSDATE TABLE THEN TO TRIGGER UID UNION UNIQUE UPDATE USER VALIDATE VALUES VARCHAR VARCHAR2 VIEW WHENEVER WHERE WITH |
Some LEA applications use the Firebird embedded database (V1.5) as an
SQL engine for dBASE tables, by loading dBASE tables into a temporary database
file. This allows standard SQL operations to be performed on the data in a
similar way to data in an Oracle database, and improves search and update speed
for large tables.
The Firebird project is an open-source relational SQL
database. Information and downloads are available from
www.ibphoenix.com and
www.firebirdsql.org. The database
engine is wholly contained within the DLL gds32.dll.
Temporary
Firebird database files are created with a .GDB extension in the SCRATCH
folder on each PC
The following list of words are reserved for use in Firebird SQL. You should avoid using any of these words as dBASE field names.
| ABS ACTION ACTIVE ADD ADMIN AFTER ALL ALTER AND ANY AS ASC ASCENDING AT AUTO AUTODDL AVG BASED BASENAME BASE_NAME BEFORE BEGIN BETWEEN BIGINT BLOB BLOBEDIT BOOLEAN BOTH BUFFER BY CACHE CASCADE CAST CHAR CHARACTER CHARACTER_LENGTH CHAR_LENGTH CHECK CHECK_POINT_LEN CHECK_POINT_LENGTH COLLATE COLLATION COLUMN COMMIT COMMITTED COMPILETIME COMPUTED CLOSE CONDITIONAL CONNECT CONSTRAINT CONTAINING CONTINUE COUNT CREATE CSTRING CURRENT CURRENT_CONNECTION CURRENT_DATE CURRENT_ROLE CURRENT_TIME CURRENT_TIMESTAMP CURRENT_TRANSACTION CURRENT_USER CURSOR DATABASE DATE DAY DB_KEY DEBUG DEC DECIMAL DECLARE DEFAULT DELETE DESC DESCENDING DESCRIBE DESCRIPTOR DISCONNECT DISPLAY DISTINCT |
DO DOMAIN DOUBLE DROP ECHO EDIT ELSE END ENTRY_POINT ESCAPE EVENT EXCEPTION EXECUTE EXISTS EXIT EXTERN EXTERNAL EXTRACT FALSE FETCH FILE FILTER FLOAT FOR FOREIGN FOUND FREE_IT FROM FULL FUNCTION GDSCODE GENERATOR GEN_ID GLOBAL GOTO GRANT GROUP HAVING HELP HOUR IF IMMEDIATE IN INACTIVE INDEX INDICATOR INIT INNER INPUT INPUT_TYPE INSERT INT INTEGER INTO IS ISOLATION ISQL JOIN KEY LEADING LC_MESSAGES LC_TYPE LEFT LENGTH LEV LEVEL LIKE LOGFILE LOG_BUFFER_SIZE LOG_BUF_SIZE LONG MANUAL MAX MAXIMUM |
MAXIMUM_SEGMENT MAX_SEGMENT MERGE MESSAGE MIN MINIMUM MINUTE MODULE_NAME MONTH NAMES NATIONAL NATURAL NCHAR NO NOAUTO NOT NULL NUMERIC NUM_LOG_BUFS NUM_LOG_BUFFERS OCTET_LENGTH OF ON ONLY OPEN OPTION OR ORDER OUTER OUTPUT OUTPUT_TYPE OVERFLOW PAGE PAGELENGTH PAGES PAGE_SIZE PARAMETER PASSWORD PERCENT PLAN POSITION POST_EVENT PRECISION PREPARE PRESERVE PROCEDURE PROTECTED PRIMARY PRIVILEGES PUBLIC QUIT RAW_PARTITIONS RDB$DB_KEY READ REAL RECORD_VERSION RECREATE REFERENCES RELEASE RESERV RESERVING RESTRICT RETAIN RETURN RETURNING_VALUES RETURNS REVOKE RIGHT ROLE ROLLBACK ROWS ROW_COUNT RUNTIME SAVEPOINT SCHEMA SECOND SEGMENT SELECT SET SHADOW SHARED |
SHELL SHOW SINGULAR SIZE SMALLINT SNAPSHOT SOME SORT SQLCODE SQLERROR SQLWARNING STABILITY STARTING STARTS STATEMENT STATIC STATISTICS SUB_TYPE SUM SUSPEND TABLE TEMPORARY TERMINATOR THEN TIES TIME TIMESTAMP TO TRAILING TRANSACTION TRANSLATE TRANSLATION TRIGGER TRIM TRUE TYPE UNCOMMITTED UNION UNIQUE UNKNOWN UPDATE UPPER USER USING VALUE VALUES VARCHAR VARIABLE VARYING VERSION VIEW WAIT WEEKDAY WHEN WHENEVER WHERE WHILE WITH WORK WRITE YEAR YEARDAY |
LEA programs can import and export data from tables into comma-delimited text (CSV) files, and copy data between Oracle and dBASE tables - see TBLVIEW, TBLEDIT and FLORENCE.
Some applications provide a PRMEDIT dialogue
to allow you to specify the format of the comma-delimited file.
The default
delimiters for comma-delimited files are set in the DBUTILS.INI
[startup] section:
csv delimiter specifies the default character to use to separate each field. If the decimal separator in your locale (and on your PC) is a dot, the delimiter for CSV files should be set as a comma (,). If your decimal separator is a comma, set the default delimiter to a semi-colon (;).
csv quote specifies the default character to use to surround string fields. Any csv delimiter characters inside the quotes are included as part of the string, and not parsed. The default csv quote character is the double-quote mark (").
These parameters can be displayed when importing data from a comma-delimited (CSV) file or from another table.
Field Map
This specifies the correspondence between fields in the source and destination.
Applicable for both table and CSV file import
Select from:
- Field Order (default) - the first column (field) in the source is matched with the first column in the destination, and so on.
- Field Name - match each column (field) in the source with the column of the same name in the destination.
- Custom - the columns (fields) to copy from the source to the destination are defined in a list (see Custom Field Map below)
Ignore Missing Fields In Source
Applicable for both table and CSV file import
- No - if Field Map is Field Order, this will check that the source has at least as many fields as the destination. If Field Map is Field Name this will check that each column in the destination table has a matching column name in the source. If this check fails an error message will be displayed (see below) and the import will not go ahread.
- Yes - fields missing from the source will be set to null in the destination. This may produce an error when the first row is added if the destination is an Oracle table with NOT NULL constraints.
Ignore Missing Fields In Destination
Applicable for both table and CSV file import
- No - if Field Map is Field Order, this will check that the destination has at least as many fields as the source. If Field Map is Field Name this will check that each column in the source has a matching column name in the destination. If this check fails an error message will be displayed (see below) and the import will not go ahread.
- Yes - fields missing from the destination will be discarded.
The following parameters are only applicable for CSV file import, and are not used when importing data from another table.
Delimiter
Default , (comma)
Specifies the character to use to separate field values in the csv file. If the decimal separator in your locale (and on your PC) is a dot, the delimiter for CSV files should be set as a comma (,). If your decimal separator is a comma, set the default delimiter to a semi-colon (;).Quote character
Default " (double-quote)
Specifies the default character to use to surround string fields. Any Delimiter characters inside the quotes are included as part of the string, and not parsed.Unquoted Spaces
Correctly formatted CSV files should not contain spaces unless they are part of a string - in which case they would be inside quotes. However, it is quite common to have to deal with CSV files which contain spaces. You have two options:
- Delimiter (default) - a space outside quote-marks is treated as if it is a delimiter - used to separate field values.
- Character - a space outside quote-marks is treated like any other character, and not used to delimit fields.
Date/Time Mask
For date/time fields where the format of the date/time value in the CSV file does not match the format defined on your PC (Control Panel - Regional Settings), you can specify how to translate the date/time value using a mask. This is not yet implemented.Custom Field Map
A custom field mapping allows you to specify which fields from the source to copy to the destination. Any fields which are not included in the list you enter will not be copied.
Enter a list of column names, one per line.To map the column ColName in the source table to the column of the same name in the destination table, use:ColName
To map the column named SourceColName in the source table to the column named DestColName in the destination table, use:
DestColName=SourceColName
These parameters can be displayed when exporting data from a table to a CSV file.
Delimiter
Default , (comma)
Specifies the character to use to separate field values in the csv file. If the decimal separator in your locale (and on your PC) is a dot, the delimiter for CSV files should be set as a comma (,). If your decimal separator is a comma, set the default delimiter to a semi-colon (;).Quote character
Default " (double-quote)
Specifies the default character to use to surround string fields. Any Delimiter characters inside the quotes are included as part of the string, and not parsed.Quote
Correctly formatted CSV files have each row on a single line, with delimiter characters between each field, and string values which contain spaces enclosed in quote characters. You can specify how to output the CSV file - select from
- No Fields - quote characters are not used. Fields output to the CSV will be separated only by delimiters.
- All Fields (default) - all field values in the CSV file will be enclosed in quotes, as well as separated by delimiters
- String Fields - only string fields will be quoted, other field types will just be separated by delimiters.
Date/Time Mask
For date/time fields where the format of the date/time value in the CSV file does not match the format defined on your PC (Control Panel - Regional Settings), you can specify how to output the date/time value using a mask.A date/time edit mask is constructed using these format specifiers:
Specifier Displays c The date using the short date format followed by the time using the default time format minutes and seconds) (as specified in the Regional Settings on the Windows Control Panel) d The day as a number without a leading zero (1-31) dd The day as a number with a leading zero (01-31) ddd The day as an abbreviation (Sun-Sat) dddd The day as a full name (Sunday-Saturday) ddddd The date using the short date format (from the Regional Settings section of the Windows Control Panel) dddddd The date using the long date format (from the Regional Settings section of the Windows Control Panel) m The month as a number without a leading zero (1-12). If the m specifier immediately follows an h or hh specifier, the minute rather than the month is displayed mm The month as a number with a leading zero (01-12). If the mm specifier immediately follows an h or hh specifier, the minute rather than the month is displayed mmm The month as an abbreviation (Jan-Dec) mmmm The month as a full name (January-December) yy The year as a two-digit number (00-99) yyyy The year as a four-digit number (0000-9999) h The hour without a leading zero (0-23) hh The hour with a leading zero (00-23) n The minute without a leading zero (0-59) nn The minute with a leading zero (00-59) s The second without a leading zero (0-59) ss The second with a leading zero (00-59) t The time using the short time format (hours and minutes) tt The time using the long time format (hours, minutes and seconds) am/pm The time using the 12-hour clock for the preceding h or hh specifier, followed by "am" for any hour before noon, or "pm" for any hour after noon. The am/pm specifier can use lower, upper, or mixed case, and the result is displayed accordingly a/p The time using the 12-hour clock for the preceding h or hh specifier, followed by "a" for any hour before noon, or "p" for any hour after noon. The a/p specifier can use lower, upper, or mixed case, and the result is displayed accordingly ampm The time using the 12-hour clock for the preceding h or hh specifier, followed by the AM specifier for any hour before noon, or the PM specifier for any hour after noon (from the Regional Settings section of the Windows Control Panel) / The date separator character from the Regional Settings section of the Windows Control Panel : The time separator character from the Regional Settings section of the Windows Control Panel 'xx'/"xx" Characters enclosed in single or double quotes are displayed as-is, with no formatting changes Format specifiers may be written in uppercase or lowercase letters; both produce the same result. If the string given by the Format parameter is empty, the date and time value is formatted as if a c format specifier had been given.
Column Headers
YES/NO - specify whether to include column headers (field names) as the first line of the export file.Export Log
YES/NO - specify whether to write a summary log of the export process. If YES, the log file will be created in the same output folder as the export file, with the same name as the export file, with extension .log. The log file will record the date/time of the export and the number of records exported.
LEA applications can display this dialogue to allow the user to alter the display order of columns from a database table, or to hide columns from the display. Note that this does not affect the underlying Oracle or dBASE table.
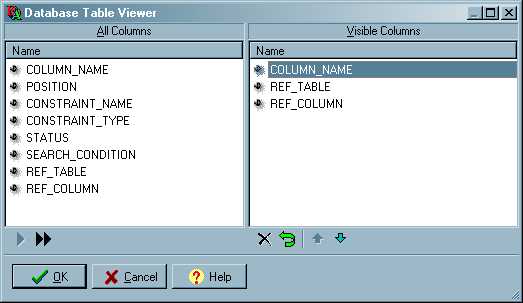
The list on the left ('All Columns) shows the columns in the order defined in the underlying table. The list on the right ('Visible Columns') shows the columns in the order in which they will be displayed.
Items can be dragged between the two lists, or you can use the buttons to add/delete items. See The Lynx Dual List component for details of the buttons.
LEA applications can display a dialogue to allow viewing and editing of 'memo' (unlimited text - Oracle CLOB/NCLOB/LONG fields and dBASE MEMO) field contents. Memo fields cannot be viewed directly in table grid displays because the contents is usually more than one line. To view the field in this dialogue, click the ...button in the grid cell for a memo field.
If the table is in edit mode, the dialogue will be displayed as above, with an OK button to confirm changes made to the text. Modifications made to the memo text will be written back to the field. If the table is in read-only mode, the dialogue will be displayed without an OK button, and editing of the memo text will be disabled.
The toolbar and popup menu have the following options:
Listed below are the error messages that may be generated by applications that use this unit
The Oracle client software is not installed on this PC, or is incorrectly configured, and direct TCP/IP connection to the Oracle database is not enabled (see Oracle Connection above).
An error occurred while copying a table from dBASE to Oracle or from Oracle to dBASE.
Oracle nested tables, object fields and array fields cannot be translated into dBASE.
Oracle does not allow the use of SQL reserved words (see list above) as table or field names.
An error occurred while attempting to append data from a comma-delimited file or table into another table.
The error may be due to one of the following causes:
- The number of fields in the source and destination does not match (for mapping fields by field order) - see Import Parameters - Field Map.
- Field names do not match in the source and destination (for mapping fields by field name or custom field mapping) - see Import Parameters - Field Map.
- The custom field mapping option has been defined, but no fieldnames have been entered.
- An error converting a data value into the type required by a field in the destination.
If an error occurs during import, the import is terminated immediately. Oracle databases can then be rolled back to remove all imported rows. For dBASE tables, added rows should be manually deleted.
See also: